The Pledge of Allegiance has been a staple of American schools for over a century, but its mandatory recitation has sparked controversy in recent years. Should the Pledge of Allegiance be optional? This question raises important issues of free speech, patriotism, and inclusivity.
Proponents of making the Pledge optional argue that it violates the First Amendment’s protection of free speech and that students should not be compelled to express a particular ideology. Opponents, however, contend that the Pledge fosters patriotism, national unity, and a sense of belonging.
Historical Context: Should The Pledge Of Allegiance Be Optional
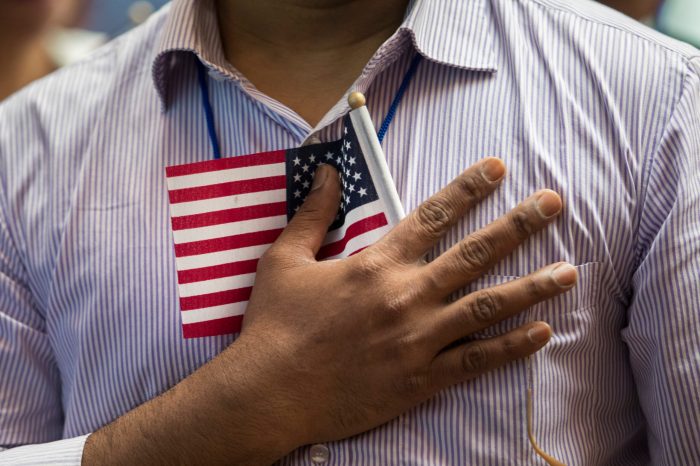

The Pledge of Allegiance was written in 1892 by Francis Bellamy, a Baptist minister and socialist. It was originally intended to promote patriotism and national unity during a time of rapid immigration and social change. The Pledge was first recited in public schools in 1893 and became mandatory in 1942. Over the years, the Pledge has been the subject of controversy and debate, with some people arguing that it is a symbol of national unity and others arguing that it is a form of forced patriotism.
Arguments for Making the Pledge Optional
One of the main arguments for making the Pledge of Allegiance optional is that it violates the First Amendment of the Constitution, which protects freedom of speech. The Supreme Court has ruled that students cannot be forced to recite the Pledge, but they can be punished for refusing to do so.
This has led to several cases of students being suspended or expelled from school for not reciting the Pledge.
Another argument for making the Pledge optional is that it is not inclusive of all Americans. The Pledge refers to the United States as a “Christian nation,” which is offensive to many non-Christians. Additionally, the Pledge does not mention any of the country’s founding principles, such as liberty, equality, or justice.
Finally, some people argue that making the Pledge optional would promote inclusivity and respect for diverse beliefs. By allowing students to choose whether or not to recite the Pledge, schools would be sending a message that all students are welcome and respected, regardless of their religious or political beliefs.
Arguments for Keeping the Pledge Mandatory, Should the pledge of allegiance be optional
One of the main arguments for keeping the Pledge of Allegiance mandatory is that it is a symbol of national unity. When students recite the Pledge, they are not only pledging their allegiance to the United States, but they are also pledging their allegiance to their fellow citizens.
This can help to create a sense of belonging and community, which is especially important in a diverse country like the United States.
Another argument for keeping the Pledge mandatory is that it helps to foster patriotism. Patriotism is a love of one’s country, and it is an important virtue for citizens to have. Reciting the Pledge can help to instill a sense of patriotism in students, which can lead them to be more involved in their communities and more likely to serve their country.
Finally, some people argue that making the Pledge optional would weaken national identity. If students are not required to recite the Pledge, they may not feel as connected to their country. This could lead to a decline in national identity, which could have negative consequences for the country.
FAQ Insights
Is it illegal to not say the Pledge of Allegiance?
No, it is not illegal to not say the Pledge of Allegiance. The Supreme Court ruled in 1943 that students cannot be forced to say the Pledge of Allegiance.
What are the arguments for making the Pledge of Allegiance optional?
Proponents of making the Pledge optional argue that it violates the First Amendment’s protection of free speech and that students should not be compelled to express a particular ideology. They also argue that making the Pledge optional would promote inclusivity and respect for diverse beliefs.
What are the arguments for keeping the Pledge of Allegiance mandatory?
Opponents of making the Pledge optional argue that it fosters patriotism, national unity, and a sense of belonging. They also argue that making the Pledge optional could weaken national identity.